Treatment Options For Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a condition in which individuals have difficulty swallowing food and liquid. In typical cases, difficulty swallowing is a complication of stroke and achalasia. Though dysphagia can occur in all groups, the condition is most likely to affect elderly individuals. It is very common for patients to feel as if there is food is lodged in the throat upon having a meal. This can be accompanied by a gurgling sound in the voice. Other symptoms include heartburn, choking, dehydration, drooling, and unintentional weight loss. Malnutrition can also occur as a result of dysphagia. Get to know the best treatment options for dysphagia now.
Esophageal Dilation
Dysphagia can occur as the result of esophageal structure becoming narrow, in which case the doctor will recommend esophageal dilation. This procedure involves the esophagus being stretched using a balloon, bougie, or guidewire. For monitoring the procedure, the doctor with fluoroscopy, which refers to the use of X-rays.
Several studies documenting the effects of dilation treatment are mentioned in a 2010 review. One study showed good or excellent results in eighteen of twenty-seven achalasia subjects. Results for six other subjects were classified as fair. Dilation on most subjects was performed using a thirty-millimeter balloon. In another study, dilation with a balloon improved symptoms in most subjects at different times. Over ninety percent saw improvement twenty-four hours following the treatment. On the other hand, results for dilation treatment have been mixed compared to surgical intervention. More up-to-date studies are necessary.
Keep reading for more on how to treat dysphagia now.
Stent Placement
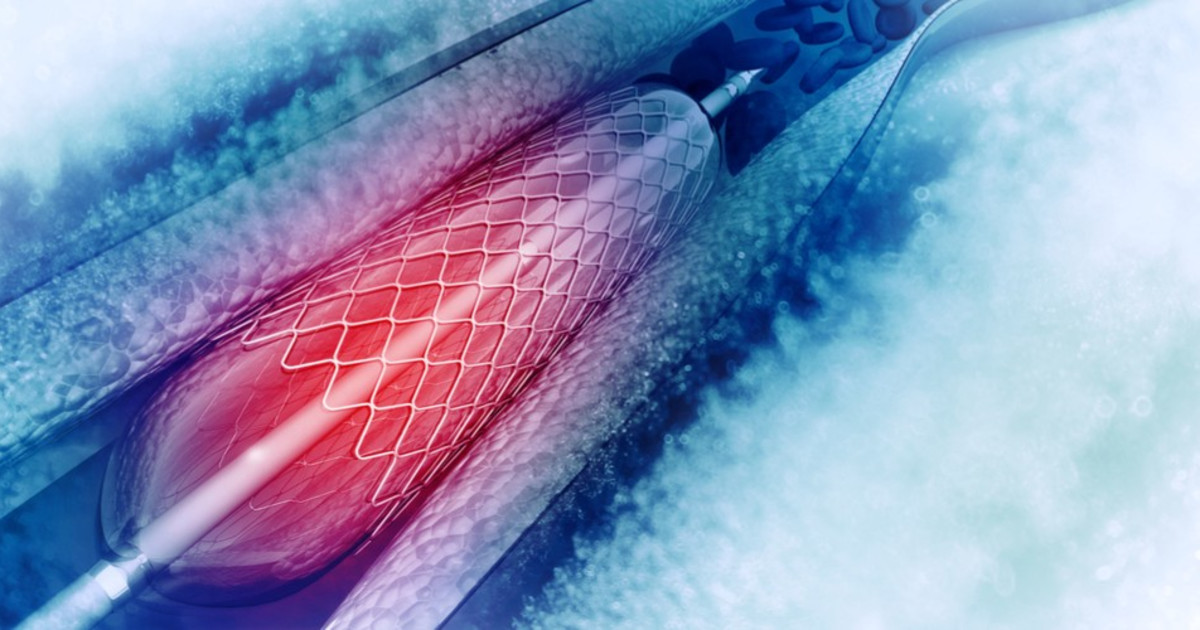
With performing a stent placement, the doctor inserts a flexible tube into the patient's esophagus. The tube will enable the narrowed area to remain open. Some research suggests stent insertion can be helpful in treating dysphagia. In a 2009 study, palliative stenting was shown to improve dysphagia in inoperable esophageal cancer subjects. Appetite was improved as well. In a study published in 2014, malignant dysphagia subjects were treated with stent featuring anti-migration features. The stent helped eliminate dysphagia for over half a year for most of the subjects.
Several complications of an esophageal stent include nausea, respiratory tract compression, gastroesophageal reflux, chest pain, and stent malposition. These complications were recorded for evaluation in a 2012 study.
Learn more about treating dysphagia effectively now.