What Is Astrocytoma?
Common Symptoms
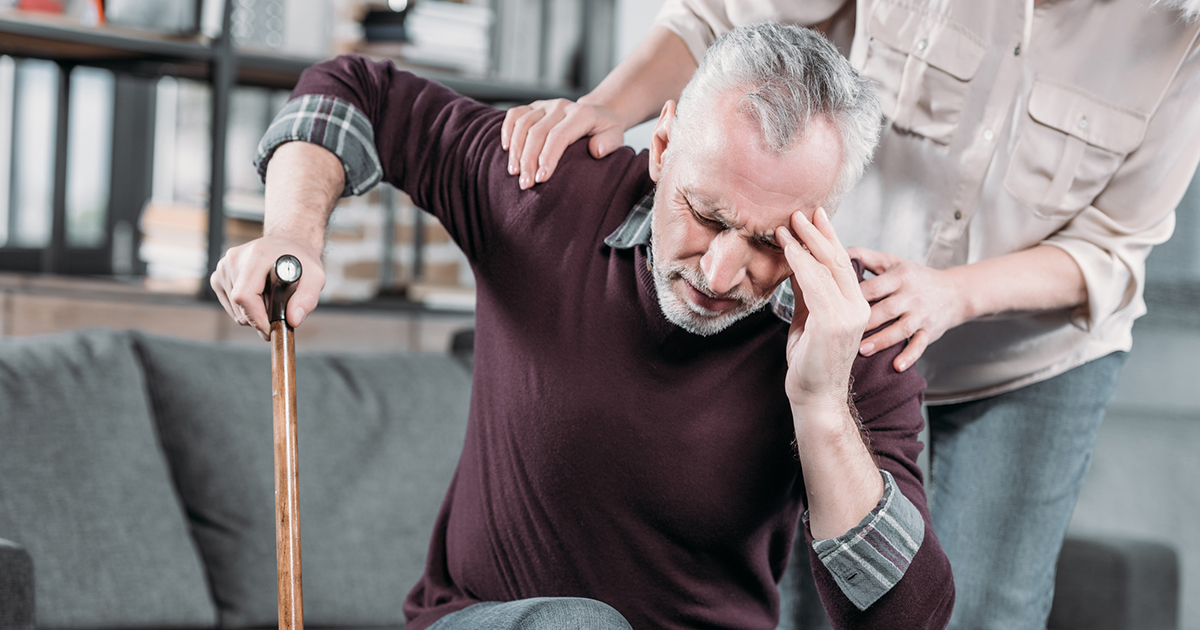
Several common symptoms occur in individuals with an astrocytoma. The severity and range of symptoms are dependent upon the location of the tumor in the brain. A slow-growing grade I or grade II astrocytoma may not manifest with noticeable symptoms since the brain can adapt to the slow-growing tumor being present over time. When symptoms do manifest, they are caused by growing pressure inside the skull on different parts of the brain or from the location of the tumor itself. Twitching and numbness in an individual's arm, leg, or face can be a manifestation of an astrocytoma, particularly when seizures are involved. Headaches that are persistent and severe, double or blurred vision, nausea and vomiting, appetite loss, mood and personality changes, changes in the ability to learn and think, gradual onset speech difficulties, and general weakness are all symptoms that are indicative of an astrocytoma. Should the astrocytoma develop in the cells located in the spinal cord, symptoms would include clumsiness in the legs, arms, and gait, along with bladder and bowel control problems.
Get familiar with the diagnostic measures for an astrocytoma next.
Diagnostic Measures
Certain diagnostic measures must be taken to identify the cause of numerous neurologically-related symptoms that may indicate the presence of an astrocytoma or other brain tumors. Careful patient history, thorough clinical evaluation, characteristic physical findings, and several specialized tests are utilized in the diagnosis of an astrocytoma. Specialized tests used to identify an astrocytoma as the underlying problem include diagnostic imaging techniques such as CT and MRI scans. The specificity and sensitivity of these imaging techniques can be enhanced when intravenous contrast medium is administered to the patient during the scans. Careful administration of pre-medication can help physicians overcome a patient's allergy to dye in cases where contrast scans are necessary. Neuroimaging tests help a physician evaluate the size, location, and other characteristics of a patient's tumor. Once a tumor is confirmed, a brain tissue biopsy procedure is carried out to obtain a sample that is sent to the laboratory for a microscopic examination of the malignant cells to identify the tumor grade and type.
Discover how to treat an astrocytoma, along with the patient prognosis, next.
