Causes And Risk Factors Associated With Muscle Cramps
Narrowed Arteries
Narrowed arteries typically cause cramps while an individual is exercising or directly after they finish exercising. The cramps rarely persist for long after they stop exercising and rest. If they do persist, the affected individual may need medical attention. The legs are supplied with blood through several different arteries. Exercising can cause these arteries to narrow, which means that individuals may not receive the blood supply they need. This is doubly compounded because the muscles need more oxygen during exercise, and oxygen is delivered by red blood cells.
Cramps from this phenomenon can occur throughout the legs and feet. Peripheral artery disease often causes cramping pain in the calves, thighs, or hips. The narrowed arteries are only noticeable during exercise, since the muscles require more oxygen. In this case, cramps are the muscle warning the brain it cannot sustain the current activity level.
Learn more about the causes of muscle cramps now.
Dehydration
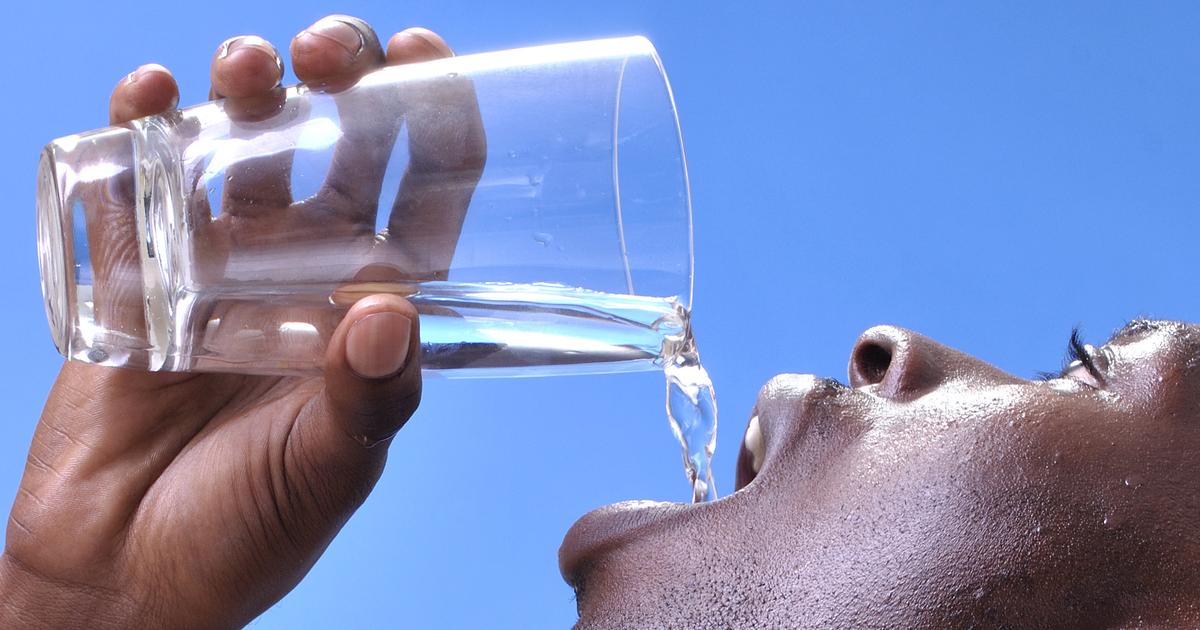

Many individuals know feeling thirsty is a common warning sign of dehydration. However, there are other signs of dehydration, including muscle cramps. When the body is depleted of fluid, its natural cooling mechanisms do not work, leading to overheating and heat illness. Heat illness is especially common in individuals who exercise in hot conditions. Experts say that as individuals get hotter, their muscle cramps will become more intense. Normally, the body cools itself naturally by releasing fluid and using water to cool off the internal structures. However, a lack of water can lead to overheating, similarly to how a car engine overheats if there is no coolant. The increased temperature causes the muscles to seize up and spasm.
Cramping from increased temperature is a serious sign of heat illness and might require emergency treatment. If an individual's muscles are too hot to function, their internal organs also are. However, cramping is not always the result of increased internal temperature. Electrolyte imbalances, also caused by dehydration, can keep the muscles from adequately performing.
Keep reading to learn more about the risk factors linked to muscle cramps now.