Common Symptoms Of Mastocytosis
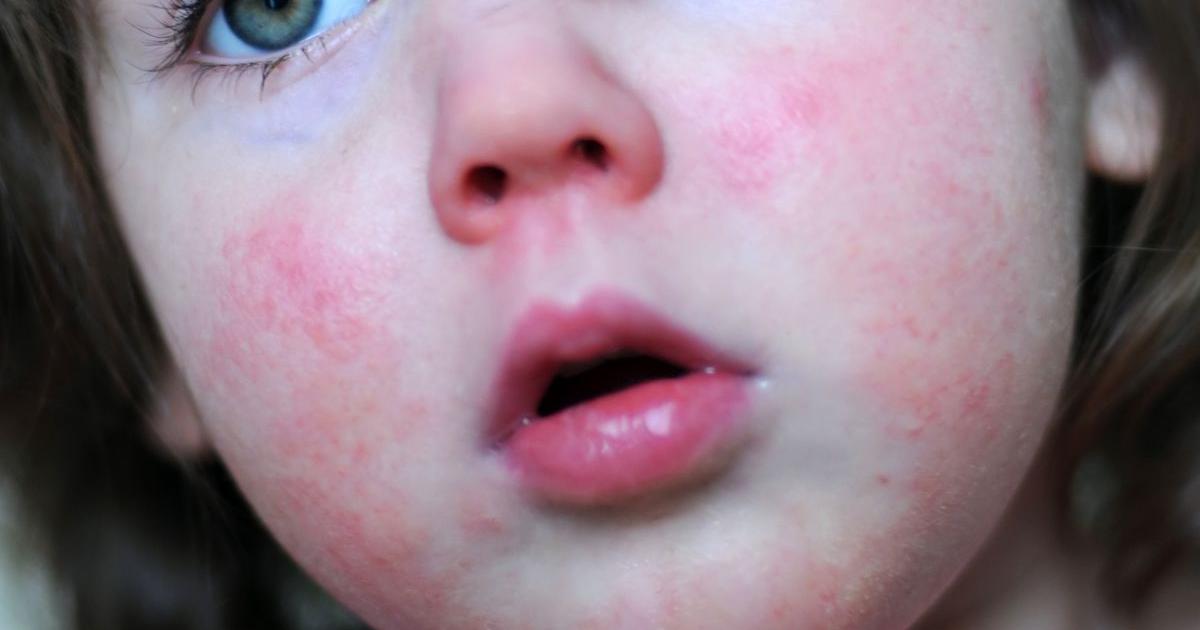
Facial Flushing
Facial flushing is a symptom of mastocytosis that occurs at some point in the majority of individuals affected by the condition. Facial flushing in systemic mastocytosis has been described as a bright red coloring of the face with sensations of itchiness and burning. This flushing often occurs alongside gastrointestinal symptoms that are also the result of systemic mastocytosis. Facial flushing in affected individuals tends to occur abruptly and quickly. Reddish-brown bumps have occurred as a feature of the facial flushing. Mastocytosis causes increased immune sensitivity to certain antigens and triggers that induce a release of histamine by excess mast cells in the affected individual's facial tissues. This produces a type of episode or allergic-like attack on the face, where histamine and other immune components cause a significant dilation of the blood vessels in the skin. The vessel dilation, histamine release, and congregation of other immune system components in the area are all implicated in giving the face a reddish appearance with burning and itching sensations.
Read more about common symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Lightheadedness
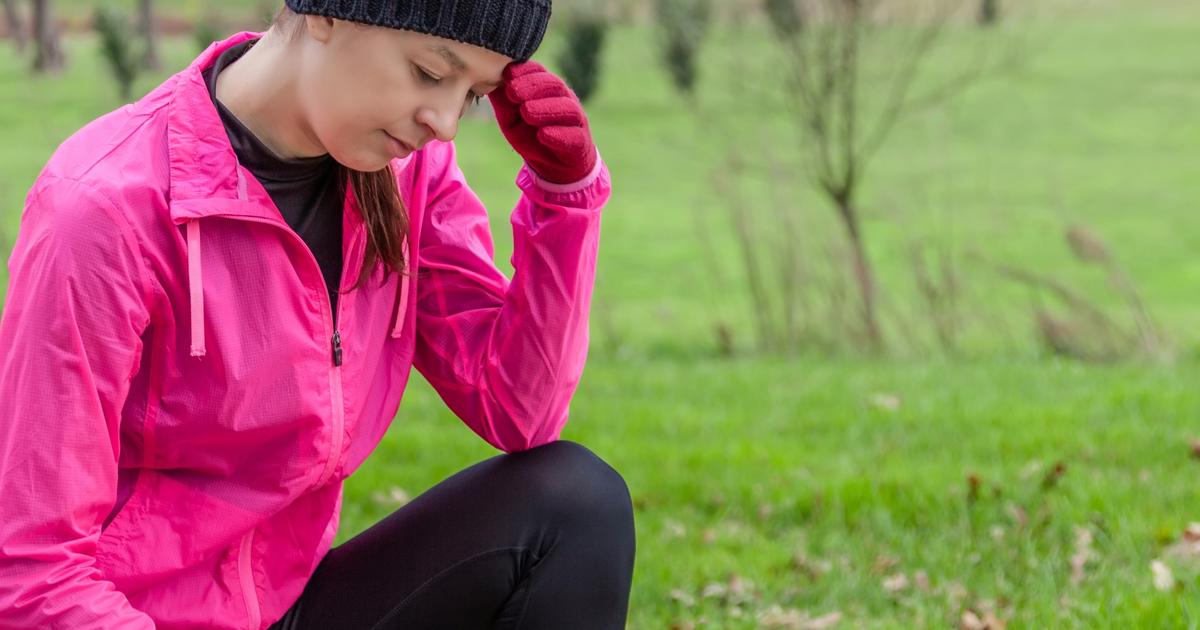

Mastocytosis is characterized by mast cell accumulation in different tissues around the body. Mast cells are certain migrant cells of an individual's immune system that feature granules of heparin and histamine. Mast cells are responsible for the regulation of blood vessel dilation, immune responses, vascular homeostasis, venom detoxification, and angiogenesis in the body. These cells have also been identified as playing a key role in the pathophysiology of asthma, gastrointestinal disorders, cardiovascular disease, allergies, anaphylaxis, and numerous types of malignancy. In a normal state, the lungs do not contain a large number of mast cell derivatives. When an antigen comes in contact with the respiratory tract lining, mast cell derivatives are summoned to the respiratory endothelium. Those affected by mastocytosis already have an excess amount of mast cells that may be concentrated in the lungs, exasperating the symptoms that occur upon their activation. Bronchial constriction and edema cause a decrease in lung capacity, which results in reduced blood oxygen concentration. Low oxygen concentrations in the blood cause deprivation of oxygen in the brain tissues that may result in lightheadedness. Hypotension from vasodilation has also been implicated as a cause of this symptom in mastocytosis.
Keep reading to learn more about the major symptoms of mastocytosis now.