How To Diagnose And Treat Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a condition characterized by a build-up of pressure inside of one of the compartments in an individual's body separated by the fascia or tough connective tissue membrane. The fascia functions to hold all of the individual's tissues and organs in their respective places throughout the body, so it is not flexible and does not expand readily. When the pressure inside of the fascia of a compartment in the body increases, the blood vessels that feed all of the comprising tissues become compressed. This malfunction results in blood flow interruption to the organ, nerve, and muscle cells that cause them to become damaged. Indications an individual is being affected by compartment syndrome include tingling and burning sensations in the affected area, a tight or full feeling of muscles in the area, intense and persistent pain, numbness, swelling, and bruising in the affected area.
Read about how to diagnose and treat compartment syndrome now.
Removal Of Casts And Other Restrictions
A physician can diagnose an individual's compartment syndrome by the removal of casts and other restrictions to evaluate the compartment in question. An estimated seventy-five percent of all acute compartment syndrome cases are precipitated from a broken or fractured arm or leg. Inflammation of the tissues around the broken bone can cause the area to swell, as well as cause edema or an accumulation of fluid. This mechanism alone can cause compartment syndrome in the affected limb. Compartment syndrome can also occur later on as a result of surgery done to treat the break or an incorrectly set cast or splint. Surgery is sometimes required to reset the bone and insert hardware to ensure the bone heals correctly. The inflammation from surgery can cause compartment syndrome after the limb has been set in a cast or splint. When an individual's limb is placed in a cast that is too tight, this mechanism alone can cause the development of compartment syndrome. Since most bone breaks with or without the addition of surgical treatment are secured with a cast or splint, these devices have to be removed for a physician to make an accurate compartment syndrome diagnosis.
Continue reading to discover treatments for compartment syndrome.
Fasciotomy
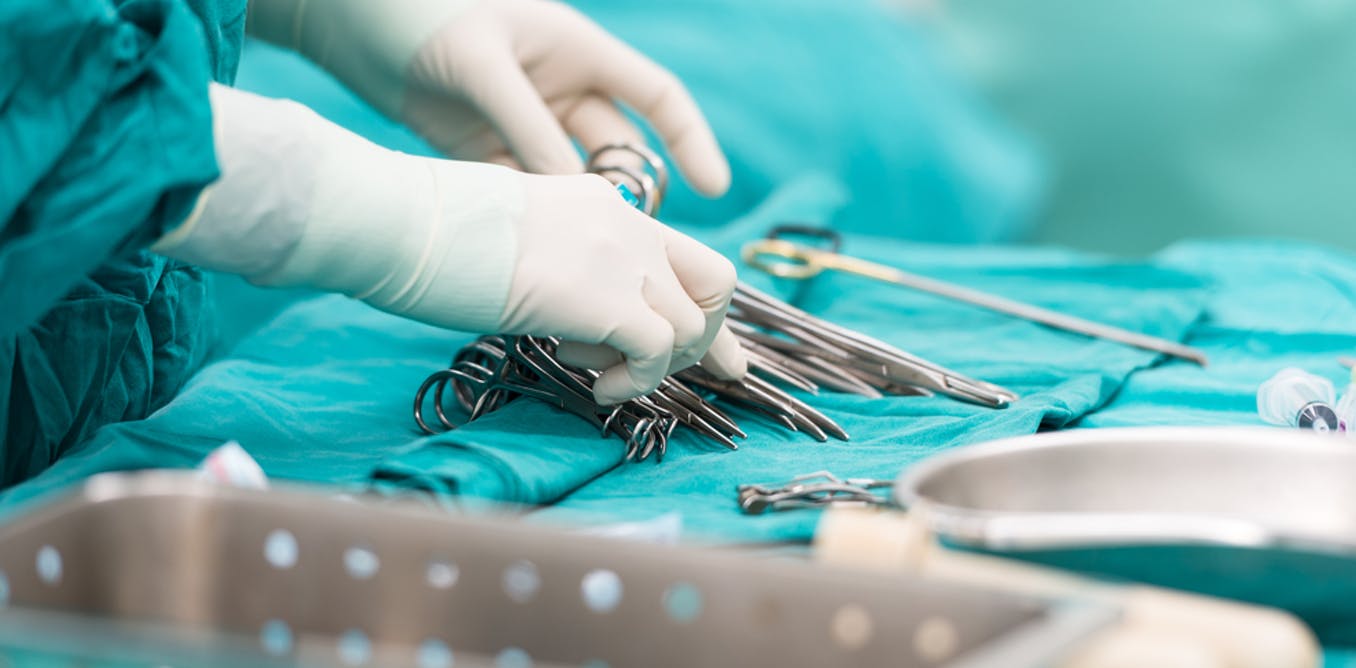
A fasciotomy is a surgical procedure often used to treat individuals affected by compartment syndrome. A fasciotomy involves surgically opening the affected fascia to decrease pressure on the containing organs and tissues. This type of surgery is most often done in the leg, but it can also be used to treat compartment syndrome that occurs in the foot, hand, arm, or abdomen. For the treatment of compartments of the arm or leg, the surgeon makes one incision in the skin on top of the affected compartment. This incision usually spans the entire length from one joint to the next of the affected limb. The fascia is cut in a similar fashion with one incision that runs the same length as the first. Any tissue that has suffered necrosis or died is then extracted from the compartment. The fascia and skin are then sewed back together with very loose stitching, keeping the wound open. The area is then wrapped in a loose dressing and closely monitored so any more dead tissue can be removed, the wound can be cleaned, the stitches can be tightened, and a new dressing can be applied. This process of tightening the stitches and wound make take up to two weeks. If compartment syndrome has been caused by recent surgery, the existing wound is used if possible.
Keep reading to learn about more tips for treating compartment syndrome now.