Treatments For An Epidural Hematoma
An epidural hematoma is a medical condition that occurs after head trauma. Upon impact, the brain bounces inside the skull, causing tears and damage to its lining and blood vessels, resulting in bleeding inside the skull. A mass of blood may form between the brain and the skull. This mass is called an epidural hematoma. The mass of blood increases pressure on the brain, which leads to swelling, which in turn leads to more pressure. The initial head trauma already caused a brain injury, and the epidural hematoma might make the brain damage worse. Untreated hematomas can be life-threatening, or at the very least, permanently debilitating. Fortunately, there are some successful treatment methods. Get familiar with them now.
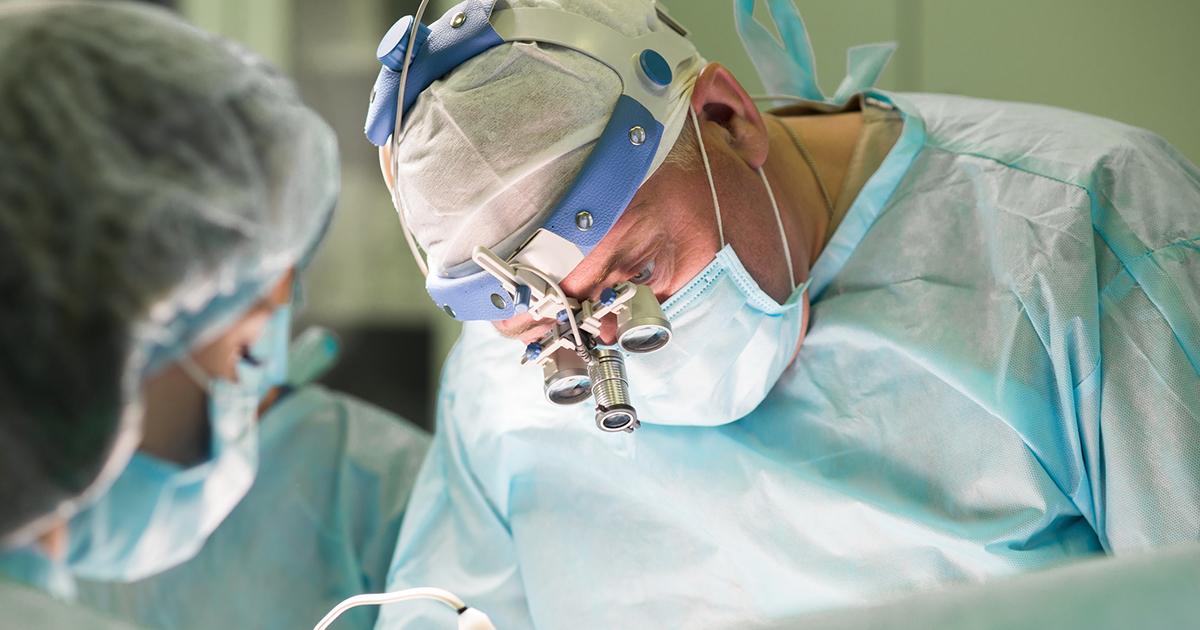
Surgery
In the majority of cases, the main course of action doctors will suggest is surgery to remove the hematoma. The procedure tends to involve a craniotomy, where a surgeon opens up a small portion of the patient's skull to remove the epidural hematoma. This helps reduce the pressure inside the skull.
Another common surgical procedure is aspiration. This type of operation is recommended less often, as it tends to work in cases where the hematoma is particularly small. If the epidural hematoma is already increasing the pressure on a person's brain, it's too big to be removed through aspiration.
When performing an aspiration operation, the surgeon cuts a small hole into the patient's skull and removes the hematoma through suction. This is a far less invasive operation, and as such, it has a much faster recovery time. But it should only be used when the hematoma is small enough. If a surgeon uses the wrong procedure, they might fail to remove the entire hematoma, which would require a second operation at best, and cause critical complications at worst.
Continue to learn more about treating epidural hematomas.
Medication
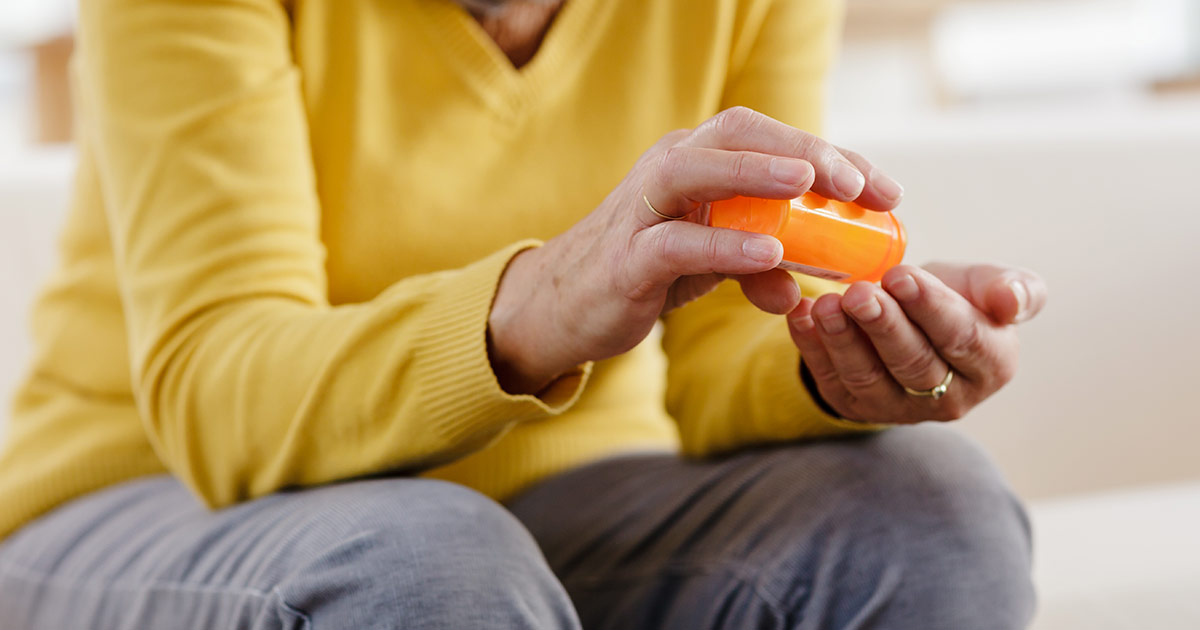

Unless the epidural hematoma is causing critical pressure on the brain, an operation generally won't be performed without the patient taking medication beforehand. Doctors will generally prescribe drugs that help reduce intracranial pressure and overall inflammation. One group of medication is called hyperosmotic agents, including hypertonic saline, glycerol, and mannitol, which are designed to reduce the swelling in a person's brain. One of the most common complications of a head injury is the potential for seizures, which is why doctors might prescribe anti-epileptics and anti-seizure drugs. Depending on the severity of trauma, patients might need to take these medications for a long time. Some patients use them for years, although this is usually only the case if they have already experienced seizure-related complications.
Continue for the next way to treat an epidural hematoma.