Signs Of A Branchial Cleft Cyst And How It's Diagnosed
Swelling Or Tenderness Around The Neck
Swelling or tenderness around the neck is often the first sign that brings a patient with a branchial cleft cyst to the doctor. These cysts are normally found on one side of the neck, though they do sometimes present as pairs. This swelling is often associated with a cold or another infection that requires the sinuses to drain. The cyst fills with mucus, becoming swollen and uncomfortable. Depending on the size and placement, swelling can interfere with swallowing. When the cyst is infected, its walls become thicker making it even more noticeable. If a doctor suspects infection, they will prescribe antibiotics. In more extreme cases, the doctor will order incision and drainage of the cyst.
Uncover precisely how a branchial cleft cyst is diagnosed now.
Diagnostic Imaging Tests
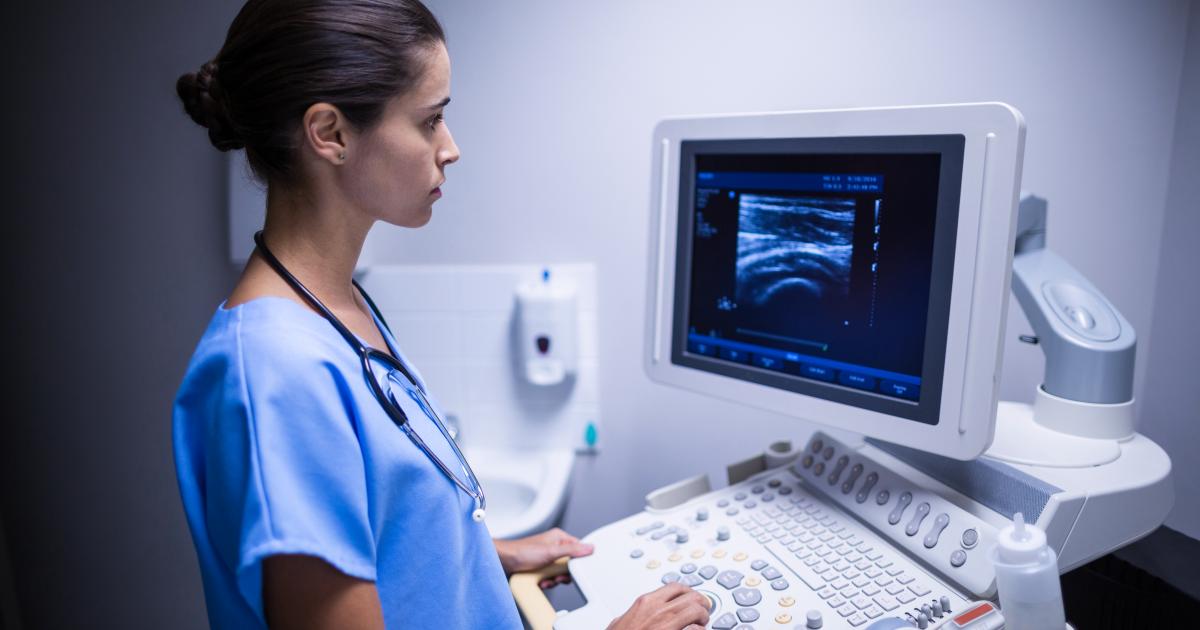
Diagnostic imaging tests are an important tool in diagnosing a branchial cleft cyst. The primary concern is making certain the lump is a relatively harmless cyst and not something more serious like a cancerous growth. The most common tests ordered are ultrasound, CT, and MRI scans. Of these three, the MRI gives the clearest image of the cyst. When doctors examine the scans, they hope to see a liquid-filled structure and not a solid lump. A cyst will usually have a well-defined, smooth oval shape without the irregularities of a cancerous growth. Another indicator of a cyst as opposed to cancer is the lack of independent blood supply to the structure.
Learn about another way in which a branchial cleft cyst is diagnosed now.
