How To Diagnose And Treat Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a disorder of autoimmunity where an individual's immune system inappropriately attacks the healthy tissues that protect the nerve cells. The myelin sheath is a type of protective fatty insulation that helps shield nerves from damage and allows for the smooth and uninterrupted transmission of impulses from one nerve to the next. The trigger of CIDP in some individuals is not currently known and has no infectious or genetic association. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy is more common in older adults than it is in any other age group, and it is more prevalent in men than it is in women. Individuals with CIDP experience symptoms including gradual limb weakening, reflex loss, balance loss, numbness, tingling, and difficulty walking. CIDP can be diagnosed using a physical exam, blood tests, urine tests, nerve conduction study, and a lumbar puncture.
There are several ways chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy can be diagnosed and treated. Reveal them now.
Diagnostic Tests
It can be difficult for a physician to narrow down a diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in an individual who presents with symptoms characteristic of this rare neurological disorder. An individual who has symptoms of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy may be brushed off until their symptoms become so pronounced that they interfere with everyday activities and responsibilities. The only diagnostic tests used specifically to make a chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy diagnosis are a spinal tap, nerve biopsy, and electromyography. A chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy patient may exhibit abnormally high levels of certain proteins in their cerebrospinal fluid that can be detected with the use of a spinal tap procedure. Patients will also present with a pattern of multifocal demyelination when they undergo a nerve conduction study or electromyography.
Reveal treatments for this condition now.
Plasmapheresis
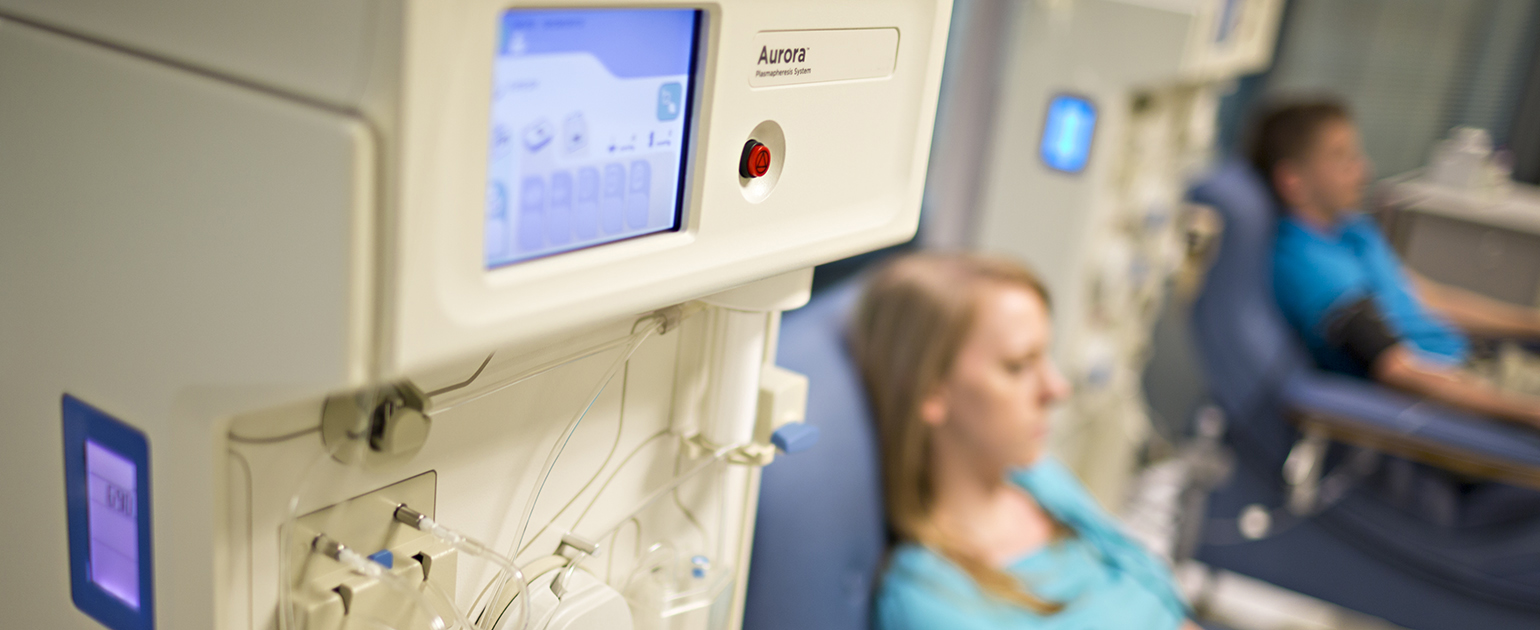
Plasmapheresis is a treatment method where the patient's blood is removed from the body and plasma is separated from the rest of the blood inside of a specialized machine. The plasma portion of the blood is replaced with a mixture of saline and albumin before it is mixed with the rest of the blood and sent back into the patient's body. The mechanism of this type of blood filtering is similar to what occurs with dialysis. The objective of this treatment is to remove the components of the blood responsible for eliciting the inappropriate attack on the healthy myelin sheathing. Numerous different types of autoantibodies are implicated in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. The most common autoantibodies identified in affected individuals include antibodies against peripheral myelin protein two or PMP2, peripheral myelin protein 22 or PMP22, and myelin protein zero or MPZ. The regular removal of these antibodies from an affected individual's blood via plasmapheresis can help alleviate symptoms of CIDP.
Uncover more treatments for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy now.