What Are The Types Of Dystonia?
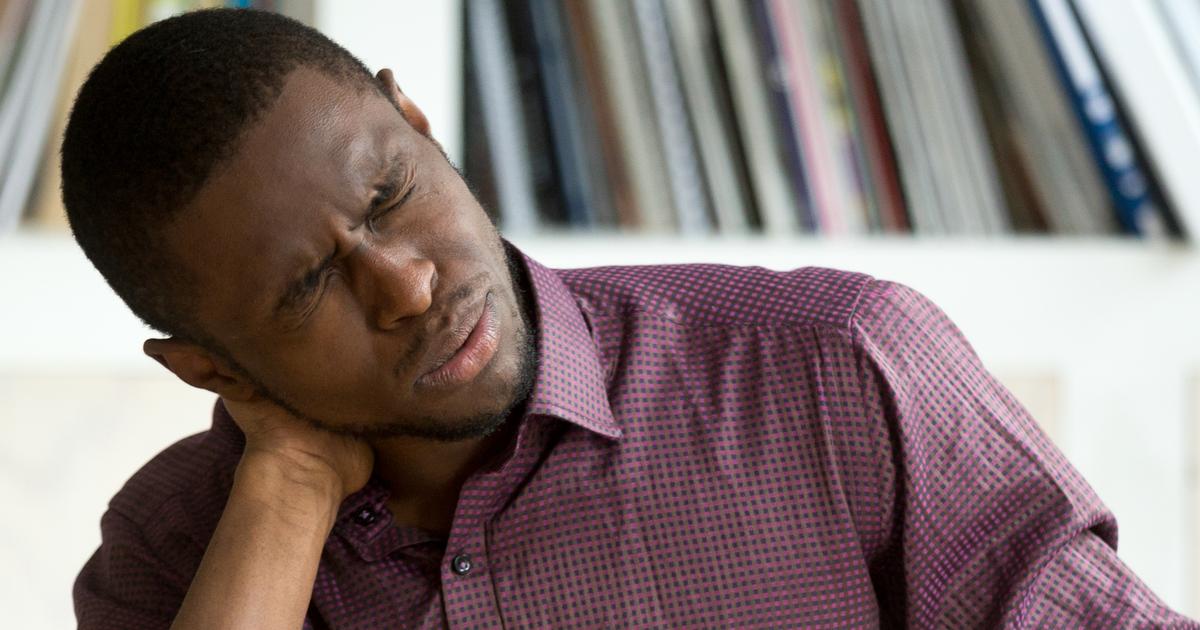
Cervical Dystonia
Cervical dystonia is a form of dystonia characterized by involuntary contractions of an individual's muscles in their neck. This involuntary muscle contraction in the neck causes the patient's head to twist or turn to one side. It is not uncommon for the contractions to produce an involuntary and repetitive movement of the head in a forward and backward motion. These abnormal movements can lead to several complications and are very painful. Headaches, backaches, shoulder aches, and pain in the neck are common occurrences in cervical dystonia patients. Some individuals who have cervical dystonia experience a spread of their symptoms to another nearby part of the body, most often involving the trunk, jaw, arms, and face. Cervical dystonia can cause a patient to develop abnormal bone growths referred to as spurs on their spine. Spurs compress the nerves that run through the spine and cause weakness in the limbs.
Read more about the various types of dystonia now.
Spasmodic Dystonia
Spasmodic dystonia is a type of focal dystonia that produces its main effects on an individual's vocal cords. Spasmodic dystonia can also be referred to as voice dystonia and laryngeal dystonia. Spasmodic dystonia can cause a patient's vocal cords to pull toward each other involuntarily, or it can cause them to pull away from each other. Adductor laryngeal dystonia defines when the vocal cords are forced together, and the patient produces a strangulated element when speaking. Abductor laryngeal dystonia occurs when the vocal cords are forced apart, and the patient produces a breathy element to their voice. Spasmodic dystonia can be made worse when an affected individual is tired and or anxious, unlike other forms of dystonia that are made worse when trying to perform a task. Spasmodic dystonia does not produce adverse effects when it comes to a patient's mind or their senses. Spasmodic dystonia can occur independently, or it may be paired with dystonia of a neighboring part of the body. In these cases, spasmodic dystonia would be considered a form of segmental dystonia.
Uncover more types of dystonia now.
