Warning Signs Of Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
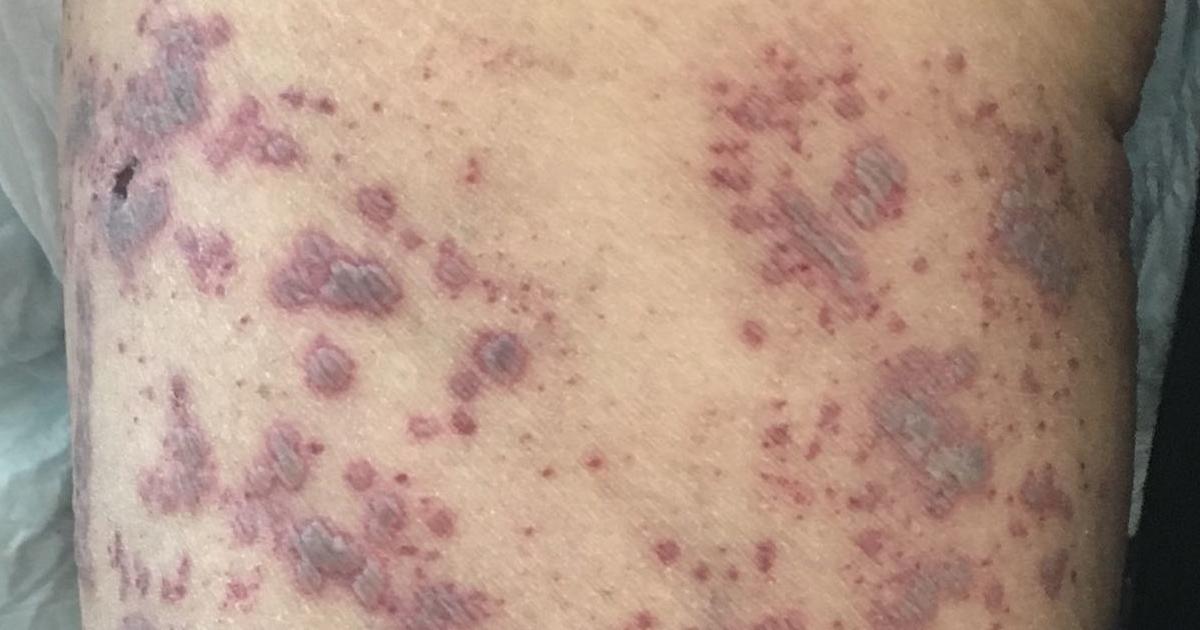
Skin Sores, Rashes, And Other Issues
The skin sores and rashes linked to granulomatosis with polyangiitis differ from individual to individual. One of the most frequently seen skin rashes in patients with this condition is referred to as palpable purpura. This type of rash occurs on the legs and consists of clusters of tiny dots that are normally purple or red. Some granulomatosis with polyangiitis patients may experience frequent bruising, and sores or cuts might be slow to heal.
Since this disorder reduces blood circulation, patients might develop Raynaud's disease, an ailment caused by inadequate blood supply to the fingers and toes. Patients with Raynaud's disease usually have an extreme sensitivity to cold temperatures, and their fingers and toes may turn purple, red, or blue during exposure to cold air. In some cases, the tissue of the fingers or toes may die, and gangrene could occur. Patients who notice any skin changes, including bruising and skin discoloration, should see a dermatologist or other specialist for prompt diagnosis. Prescription medicine may be needed to resolve some skin rashes, and lifestyle modifications are often useful for Raynaud's disease.
Continue reading to reveal more granulomatosis with polyangiitis symptoms now.
Coughing With Bloody Phlegm
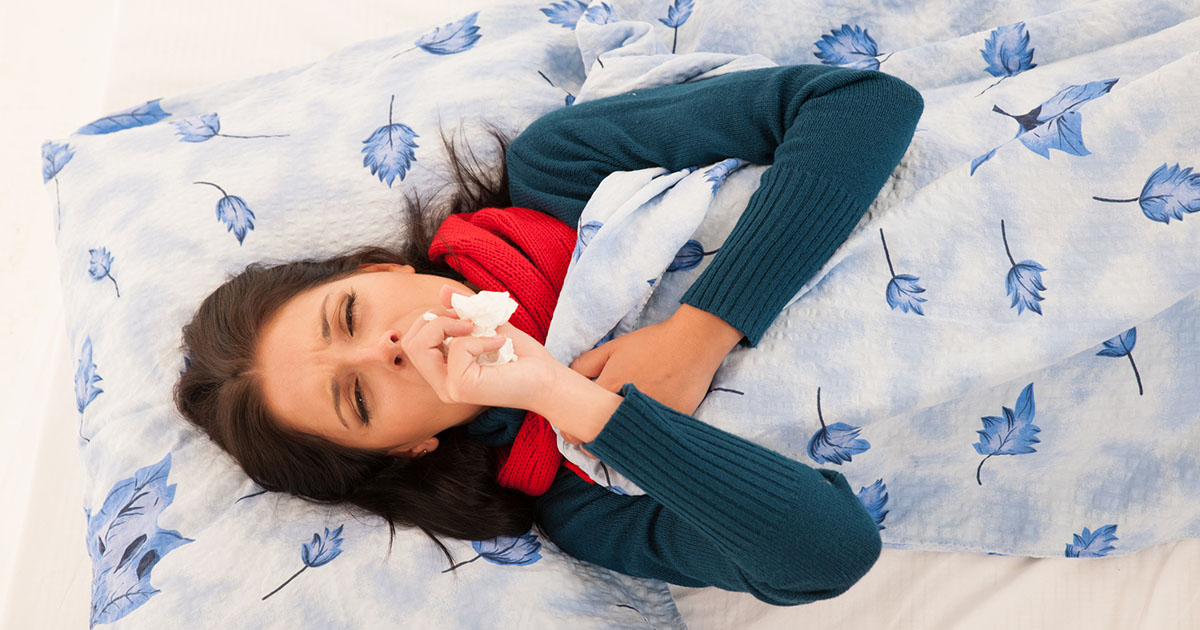

Coughing with bloody phlegm is a sign of lung involvement seen in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. This symptom can be caused by inflammation in either the upper or lower airways. Patients who experience coughing with bloody phlegm should seek an urgent evaluation from a pulmonologist or specialist since bloody phlegm may be a sign of a blood clot in the lungs. Coughing up blood could also indicate the presence of pneumonia or some heart problems. To evaluate a patient's cough, the clinician will listen to the patient's chest with a stethoscope and perform lung function studies and imaging tests. Patients may also need to have a bronchoscopy. Depending on the severity of the cough and the amount of blood a patient may be losing, treatment options could include steroids, antibiotics, a bronchial artery embolization, or the insertion of a balloon inside the airway to stop bleeding.
Get more details on the warning signs indicative of granulomatosis with polyangiitis now.