Extremely Serious Effects From Not Treating GERD
Breathing Problems
Gastroesophageal reflux disease can especially affect those who suffer from respiratory conditions such as asthma. When stomach acid is inhaled following regurgitation existing breathing issues can significantly worsen. Even if individuals do not have any underlying breathing problems like asthma, GERD has been known to cause difficulty breathing and shortness of breath, especially when it is not treated promptly. In addition to this, treating these breathing issues with gastroesophageal reflux disease at play can be very tricky, as many GERD medications can increase the risk of pneumonia. If breathing issues are an issue for a patient, they should be sure to ask their doctor for assistance in determining what treatment options are best for their case.
Discover additional complications of untreated gastroesophageal reflux disease now.
Esophageal Ulcer
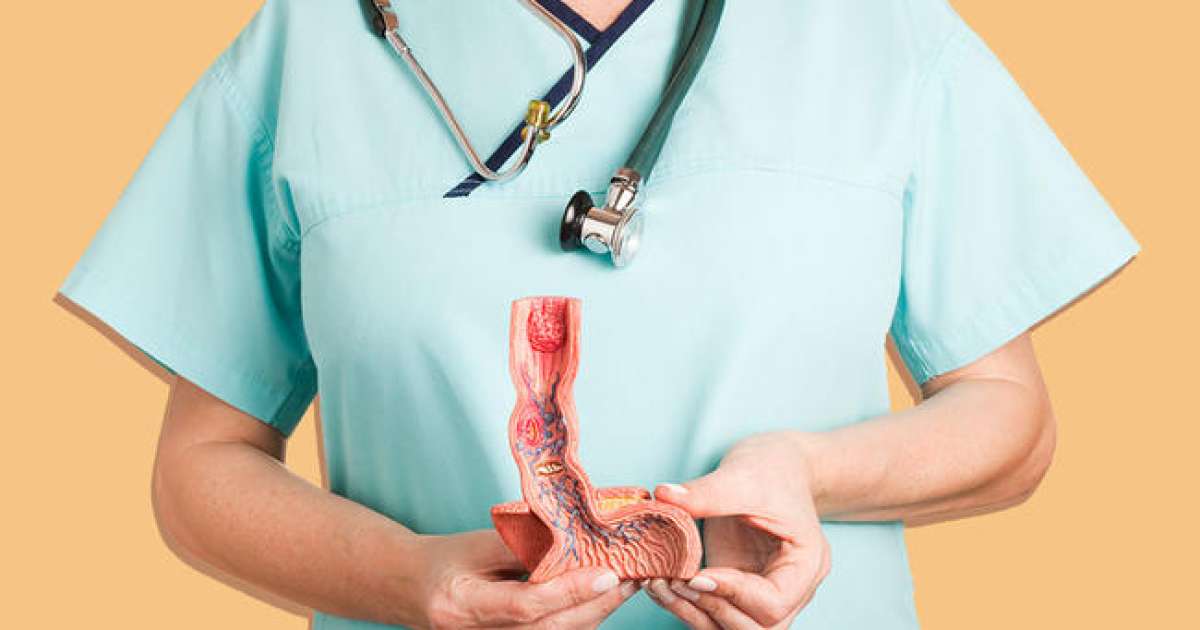
An individual may develop an esophageal ulcer as a complication of untreated gastroesophageal reflux disease. An esophageal ulcer is a painful sore that develops in the lining of the lower esophagus where the stomach meets the esophagus. The esophageal lining is not as protected as the stomach lining from corrosive stomach contents with a significant amount of stomach acid. As a result of this increased vulnerability of the esophageal lining and the mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux disease, there can be considerable erosion to the esophageal lining from recurrent exposure to stomach acid. This erosion forms an ulcer in a patient's esophageal lining. An esophageal ulcer causes patients to experience a persistent burning pain in their chest that worsens when eating certain foods or with a lack of fluid consumption. An esophageal ulcer can make it painful to swallow, cause vomiting, produce a dry cough, and cause the patient to have a sour taste in their mouth.
Uncover more GERD complications now.
