Guide To Understanding Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a spongy substance that fills the insides of the bones. It is responsible for manufacturing blood cells and storing fat. When bone marrow does not function properly, patients could develop low blood counts and other blood-related conditions such as leukemia, aplastic anemia, or myeloproliferative disorders. These disorders could result in symptoms such as fatigue, fever, easy bleeding and bruising, and shortness of breath. Patients with bone marrow issues might also notice they get colds and other infections more often than usual. Doctors may perform blood tests to investigate these symptoms. If the results show abnormalities in blood cell counts, doctors might ask for a bone marrow biopsy to be conducted. Individuals who have bone marrow abnormalities may need to have a bone marrow transplant.
The guide below describes the basic facts about bone marrow and provides information about bone marrow biopsies and donation.
What Is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow is the semi-solid substance that lines the bones. The two types of bone marrow are yellow bone marrow and red bone marrow. Red bone marrow is responsible for the production of blood cells, and yellow bone marrow helps with fat storage. At birth, babies naturally have a high percentage of red bone marrow. As individuals age, this type of bone marrow is gradually replaced with yellow bone marrow. By the time an individual reaches adulthood, red bone marrow only remains in a few bones of the body, including the ends of the femur and tibia, skull, pelvis, ribs, and ends of the humerus.
Get the details on the function of bone marrow next.
Function Of Bone Marrow
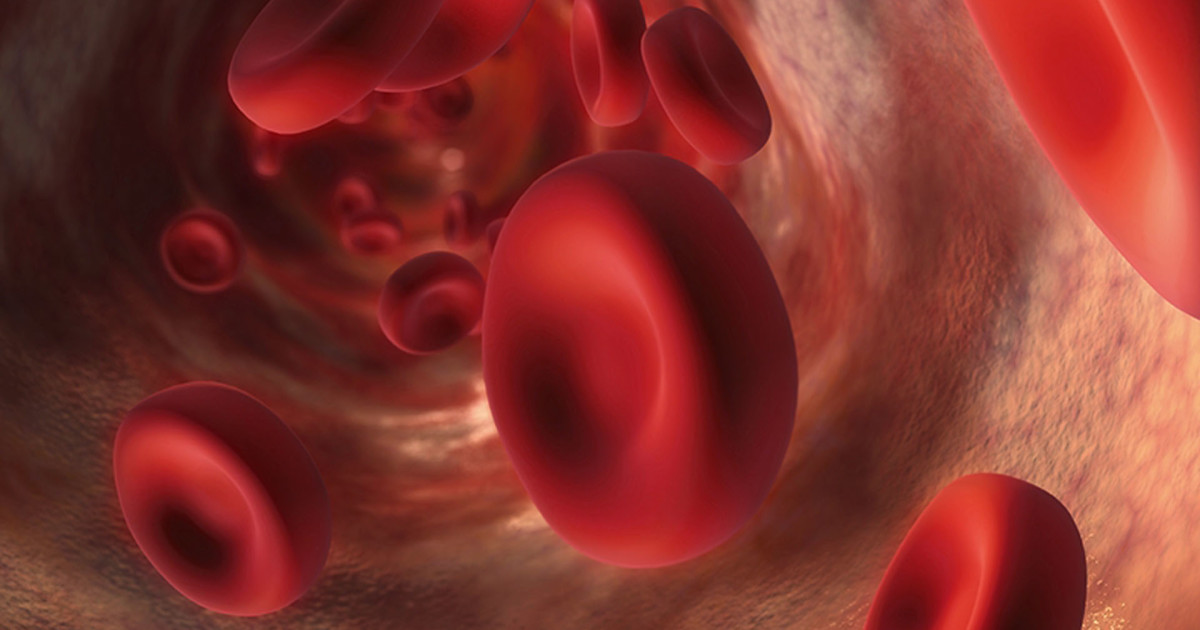
Red bone marrow contains specialized cells called hematopoietic stem cells. These cells develop to form several different types of blood cells, including red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. Red blood cells transport oxygen and nutrients around the body, and old red blood cells are also broken down by red bone marrow and the liver and spleen. Platelets promote proper blood clot formation, and white blood cells help combat infection. The newly produced blood cells manufactured by red bone marrow enter the bloodstream through special vessels known as sinusoids. Yellow bone marrow contains fats stored in adipocytes (fat cells) and that can be used as a source of energy for the body. Mesenchymal stem cells are present in yellow bone marrow, and these cells can develop into bone, cartilage, muscle cells, and fat cells. Most of an adult's bones contain yellow bone marrow.
Learn about when bone marrow biopsies are recommended next.
