Serious Side Effects Of Blood Thinners
Blood thinners are designed to allow smooth blood flow through the cardiovascular system. They can prevent the formation of blood clots or keep existing blood clots from growing. Most blood thinners are prescribed to treat heart defects, certain types of heart disease, and any medical condition that increases the likelihood of dangerous blood clots. Blood thinners can reduce the risk of a heart attack or stroke in some patients. However, they can also have potentially dangerous side effects, many of which are connected to bleeding in some fashion.
In addition to understanding the benefits of taking blood thinners, patients should also be well aware of the potential side effects they may experience so they are better able to discuss options with their doctor. Learn about the common side effects of blood thinners now.
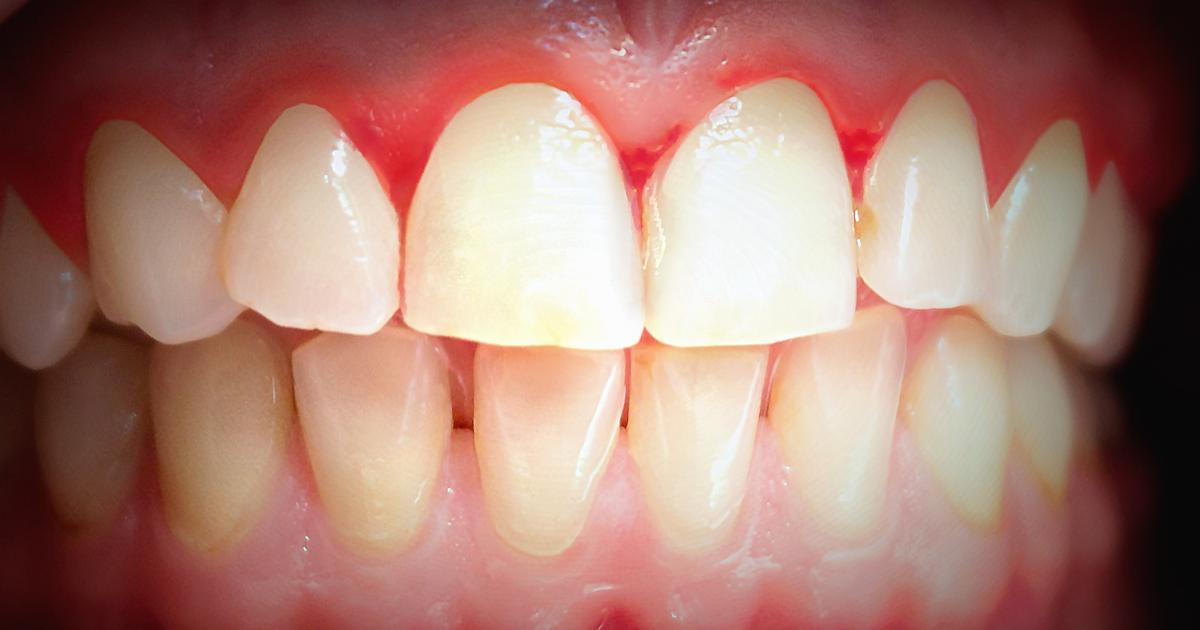
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums, which can be a side effect of blood thinners, is usually not a medical emergency. However, affected individuals may need to call their dentist if the bleeding continues without ceasing for a significant period. While bleeding gums can occur due to blood thinners, it's also important to note other factors might be at play. For instance, individuals just starting to floss may experience bleeding gums at first, and those who brush a little too hard may also see a little bit of blood. Of course, patients on blood thinners may experience more bleeding because of their medication, though they typically won't experience blood loss severe enough to warrant emergency medical attention. Regular and unexplained gum bleeding can be a sign of an underlying dental condition. Some types of gum disease that cause bleeding are easily treated, while others can lead to serious infection and decay.
Read more about the side effects of blood thinners now.
Nosebleeds
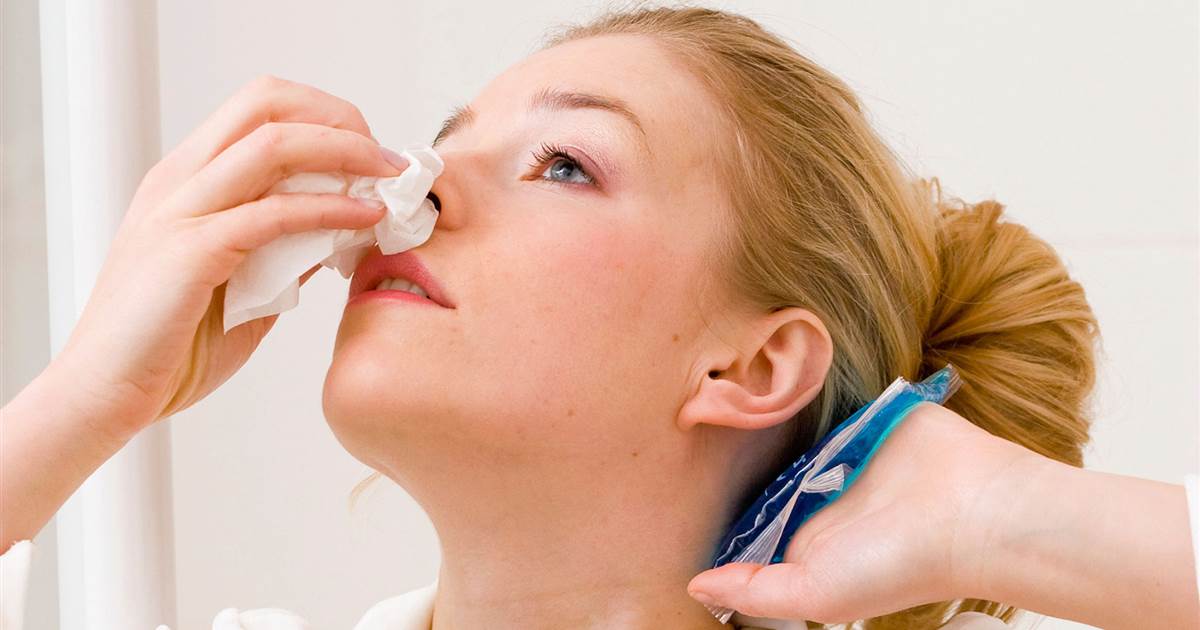
Severe nosebleeds are classed as any nosebleed that causes significant blood loss. If an individual has certain conditions that cause severe nosebleeds, blood thinners might cause dangerous side effects. The lack of clotting factors involved when taking blood thinners can make patients more susceptible to nosebleeds, and those who already experienced nosebleeds might find they increase in severity or frequency when on blood thinners. With that said, some causes of nosebleeds can't be predicted or adequately avoided, though to comm triggers include dry air and nose picking. Dried nasal membranes are more vulnerable to infections and bleeding. To avoid nosebleeds while on blood thinners, patients should stop any picking habits and consider investing in a humidifier. They should also avoid frequent use of nasal sprays if possible. Chemical irritants can lead to nosebleeds, so affected individuals should avoid directly breathing in chemical fumes and use organic cleaning products where possible.
Learn more about the various side effects of blood thinners now.